The buzz around Kaspa (KAS) has been undeniable. This open-source, decentralized, and fully scalable Layer-1 boasts the world’s fastest proof-of-work consensus mechanism, the DAG protocol (BlockDAG). Its block time, initially at one block per second, has steadily increased to a blistering ten blocks per second, promising near-instant transaction confirmations. But with rapid technological advancements come evolving economics. In the USA, the question on every aspiring crypto miner’s mind is: considering the current Kaspa mining difficulty, is it still worth plugging in those ASICs?
Mining difficulty, in essence, is a self-adjusting mechanism within a cryptocurrency’s algorithm. It reflects the computational power required to solve cryptographic puzzles and, consequently, mine a new block. As more miners join the network and contribute their hash rate, the difficulty increases, making it harder and more time-consuming to find a block. This ensures that the block creation rate remains relatively constant, regardless of the number of miners involved. Bitcoin, Ethereum (pre-merge), and Kaspa all employ this dynamic difficulty adjustment.
The initial allure of Kaspa mining stemmed from its relatively low difficulty compared to established cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. Early adopters enjoyed a higher return on investment, recouping their hardware costs faster and generating significant profits. However, the meteoric rise in Kaspa’s popularity has brought with it a surge in mining participants. This influx of miners has inevitably led to a substantial increase in mining difficulty. The higher the difficulty, the lower the reward for each miner, making profitability more challenging, especially considering electricity costs and hardware depreciation.
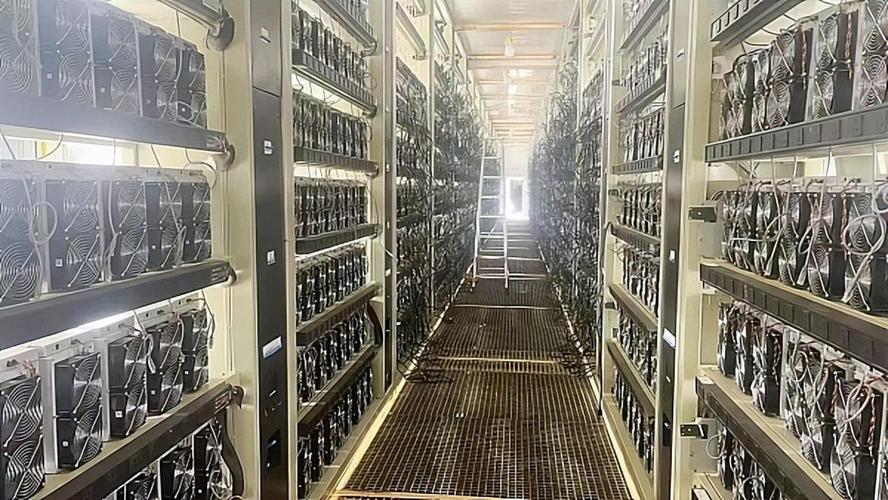

The USA presents a particularly interesting landscape for Kaspa mining. Electricity prices vary drastically across different states, ranging from relatively inexpensive hydropower-fueled regions to areas with high energy costs dependent on fossil fuels. Miners in states with low electricity rates have a significant advantage, as electricity consumption is a major operating expense. Furthermore, regulatory frameworks surrounding cryptocurrency mining differ from state to state, impacting the overall ease of doing business. Some states offer tax incentives and favorable policies to attract crypto mining operations, while others maintain a more cautious approach.
Several factors need to be considered before jumping into Kaspa mining in the USA. Firstly, the cost of mining hardware. Dedicated Kaspa ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits) are essential for efficient mining. These specialized machines are designed to perform the specific cryptographic computations required by the Kaspa algorithm. The price of these ASICs can vary depending on their hash rate, energy efficiency, and availability. Secondly, electricity costs. Conducting a thorough analysis of electricity rates in your area is crucial. A high electricity bill can quickly erode any potential profits. Thirdly, mining pool fees. Joining a mining pool allows miners to combine their hash rate and increase their chances of finding blocks. However, pools typically charge a fee for their services. Fourthly, the future price of Kaspa. The profitability of mining is directly tied to the market value of the cryptocurrency. If the price of Kaspa drops, mining becomes less profitable, and vice versa. Finally, difficulty adjustments. Continuously monitor the Kaspa network’s mining difficulty to assess the ongoing profitability of mining.
Mining machine hosting offers an alternative for those who may not have the resources or technical expertise to set up and maintain their own mining operation. Hosting providers offer various services, including hardware maintenance, security, cooling, and stable internet connectivity. By outsourcing these responsibilities, miners can focus on optimizing their mining strategies and maximizing their returns. However, hosting services also come with associated fees, which need to be factored into the overall cost analysis.
Alternatives to solo mining exist. Cloud mining, while often fraught with scams, provides the potential to rent hashing power without owning physical hardware. However, due diligence is paramount before investing in any cloud mining platform. Staking, another avenue, involves holding a certain amount of a cryptocurrency in a wallet to support the network and earn rewards. While Kaspa currently utilizes a Proof-of-Work consensus mechanism, future developments might incorporate staking or other reward systems, making it vital to stay abreast of the latest updates.
Ultimately, the decision of whether or not to mine Kaspa in the USA boils down to a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis. Conduct thorough research, consider all the factors mentioned above, and assess your risk tolerance. The cryptocurrency market is notoriously volatile, and mining is not a guaranteed path to riches. However, with careful planning and execution, Kaspa mining can still be a potentially profitable venture, especially for those with access to low electricity costs and efficient mining hardware. Stay informed, adapt to changing market conditions, and never invest more than you can afford to lose. The landscape is constantly shifting, and the keys to success lie in knowledge, diligence, and a healthy dose of calculated risk.
Leave a Reply